Kernel Density Estimation
Why KDE?
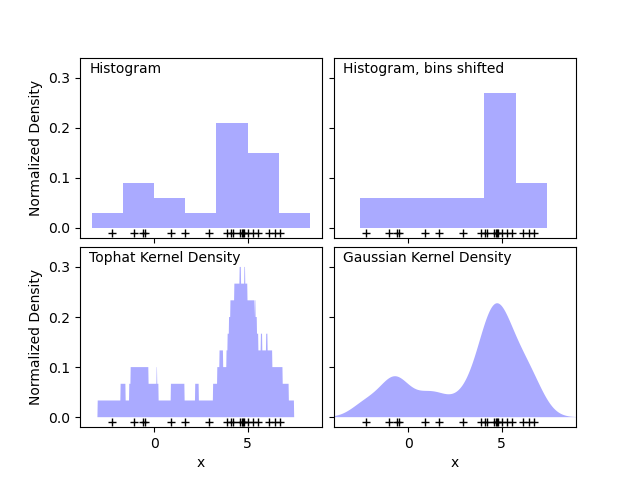
A major problem with histograms, however, is that the choice of binning can have a disproportionate effect on the resulting visualization.
Intuitively, one can also think of a histogram as a stack of blocks, one block per point. By stacking the blocks in the appropriate grid space, we recover the histogram.
But KDE is better because, instead of stacking the blocks on a regular grid, it centers each block on the point it represents, and sums the total height at each location.
Math
Mathematically, a kernel is a positive function
Free parameters of kernel density estimation:
- kernel, which specifies the shape of the distribution placed at each point
- kernel bandwidth, which controls the size of the kernel at each point. It acts as a smoothing parameter, controlling the tradeoff between bias and variance in the result. A large bandwidth leads to a very smooth (i.e. high-bias) density distribution. A small bandwidth leads to an unsmooth (i.e. high-variance) density distribution.
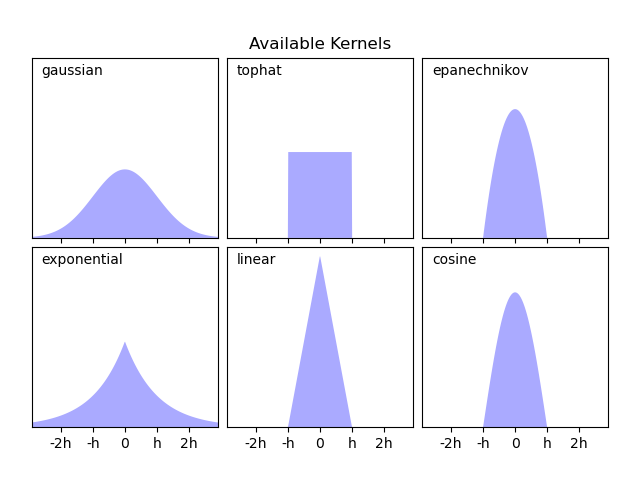
Types of Kernels